In the hustle and bustle of modern life, amid concerns about chronic diseases and other major health issues, it’s easy to overlook one’s oral health. Yet, the silent epidemic of gum disease—often ignored or dismissed as a mere inconvenience—quietly affects millions worldwide. It’s time to shine a light on this silent enemy of oral health and understand its global burden.
Understanding Gum Disease
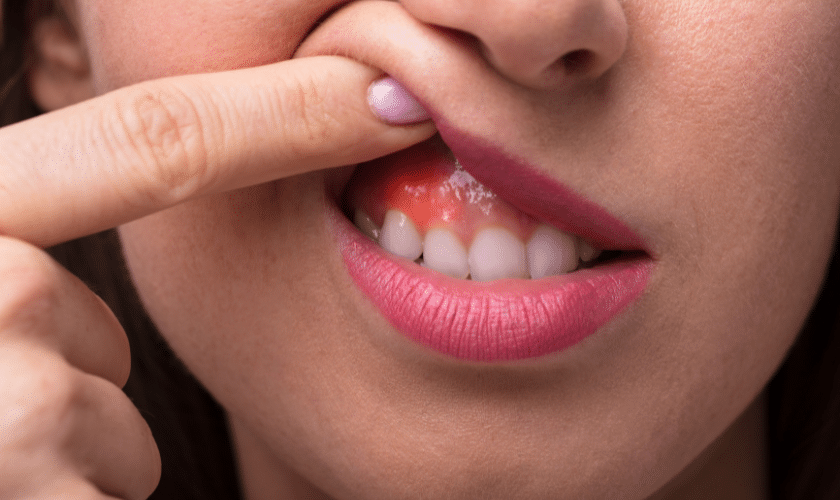
Gum disease, also known as periodontal disease, is an inflammatory condition caused by the bacteria found in plaque, the sticky film that forms on teeth. When not removed through proper oral hygiene practices such as brushing and flossing, plaque hardens into tartar, leading to gum irritation and inflammation. This condition, known as gingivitis, is the early stage of gum disease and can progress into periodontitis, a more severe form of gum disease that can result in tooth loss.
The Global Impact
Gum disease affects a significant portion of the world’s population. According to the World Health Organization, severe gum disease affects 10% to 15% of adults globally. However, the numbers may be higher in certain regions or demographic groups, making gum disease a truly global concern.
Silent Symptoms, Serious Consequences
One of the reasons gum disease is often referred to as a “silent” epidemic is because it can progress without causing noticeable symptoms until it reaches an advanced stage. While some people may experience bleeding gums, bad breath, or swollen gums, many individuals are unaware of the disease until it becomes severe.
Beyond the Mouth: The Systemic Impact
While the primary impact of gum disease is on oral health, its consequences extend beyond the mouth. Research has shown that gum disease is associated with an increased risk of several systemic health conditions, including diabetes, heart disease, stroke, and respiratory diseases. Pregnant individuals with gum disease are also at a higher risk of preterm birth and low birth weight.
Prevention and Management
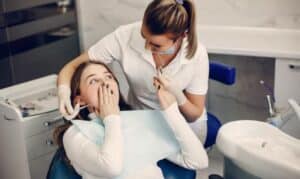
Thankfully, gum disease is preventable and manageable with proper oral hygiene and regular dental visits. Brushing teeth twice a day, flossing daily, using mouthwash, and avoiding tobacco products are key components of maintaining good oral health. Additionally, regular dental check-ups allow for early detection and treatment of gum disease, reducing the risk of complications.
Gum disease may not always receive the attention it deserves, but its impact on oral and systemic health is undeniable. By understanding the global burden of gum disease and taking proactive steps to prevent and manage it, individuals can protect their oral health and overall well-being. Remember, when it comes to gum disease, prevention is key, and early intervention can make a world of difference.